Snowdrift model in python#
A Python implementation of the model described in [DHK04]. See here for how to implement genetic value calculations in Python.
Implementing this model in C++ gives much better performance with little difference in code complexity. See here for the C++ version.
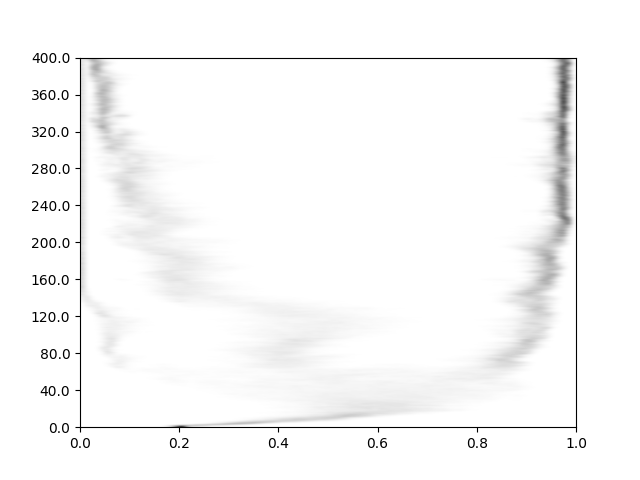
Fig. 4 Example output from the script. The y axis values are simple indexes of sampling events. Sampling occurrs every 100 generations, so multiply by that value for the generation.#
"""
Simulates the dynamics of Figure 1A from
DOI: 10.1126/science.1101456.
Final output is a plot of the phenotypes
over time, based on sampling every 100
generations.
"""
import math
import sys
import attr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import fwdpy11
@attr.s()
class PySnowdrift(fwdpy11.PyDiploidGeneticValue):
b1 = attr.ib()
b2 = attr.ib()
c1 = attr.ib()
c2 = attr.ib()
slope = attr.ib() # "stretch" parameter for sigmoid function
p0 = attr.ib() # Phenotype of a mutant-free individual
seed = attr.ib()
def __attrs_post_init__(self):
fwdpy11.PyDiploidGeneticValue.__init__(self, 1, None, None)
self.phenotypes = []
self.sig0 = (1.0 / self.slope) * math.log(self.p0 / (1.0 - self.p0))
self.rng = fwdpy11.GSLrng(self.seed)
def genetic_value_to_fitness(
self, data: fwdpy11.DiploidGeneticValueToFitnessData
) -> float:
zself = self.phenotypes[data.offspring_metadata.label]
other = int(fwdpy11.gsl_ran_flat(self.rng, 0, len(self.phenotypes)))
while other == data.offspring_metadata.label:
other = int(fwdpy11.gsl_ran_flat(self.rng, 0, len(self.phenotypes)))
zpair = zself + self.phenotypes[other]
a = 1.0 + (
self.b1 * zpair
+ self.b2 * (zpair**2)
- self.c1 * zself
- self.c2 * (zself**2)
)
return max(a, 0.0)
def calculate_gvalue(self, data: fwdpy11.PyDiploidGeneticValueData) -> float:
g = self.phenotypes[data.offspring_metadata.label]
memoryview(data)[0] = g
return g
def sigmoidize(self, g: float) -> float:
return 1.0 / (1.0 + math.e ** -(self.slope * (g + self.sig0)))
def phenotype(
self, pop: fwdpy11.DiploidPopulation, metadata: fwdpy11.DiploidMetadata
) -> float:
"""
An individual's phenotype is determined by additive effects
plus a sigmoid function that bounds trait values on [0, 1]
and places a non-mutant individual at trait value self.p0.
"""
g = fwdpy11.strict_additive_effects(pop, metadata)
return self.sigmoidize(g)
def update(self, pop: fwdpy11.DiploidPopulation) -> None:
self.phenotypes = [self.phenotype(pop, d) for d in pop.diploid_metadata]
class GetP(object):
def __init__(self):
self.data = []
def __call__(self, pop, sampler):
if pop.generation % 100 == 0.0:
md = np.array(pop.diploid_metadata, copy=False)
self.data.append(np.array(md["g"]))
def plot_trait_values(
vals, bins=100, interpolation="bicubic", vmin=None, vmax=None, tmult=1
):
parr = np.array(vals)
nruns = parr.shape[0]
phist = np.zeros((nruns, bins))
for i in range(nruns):
ph, xe = np.histogram(
parr[i].ravel(),
bins=bins,
range=[0.0, 1.0],
)
phist[i] = ph
plt.imshow(
phist,
aspect="auto",
interpolation=interpolation,
origin="lower",
cmap=plt.cm.binary,
extent=(min(xe), max(xe), 0, nruns),
vmin=vmin,
vmax=vmax,
)
plt.yticks(
np.around(np.linspace(0, nruns, 11), -1),
np.around(np.linspace(0, (nruns - 1) * tmult + 1, 11), -1),
)
plt.savefig("pysnowdrift.png")
# Branch point will be at 0.6
gv = PySnowdrift(6.0, -1.4, 4.56, -1.6, 10.0, 0.2, int(sys.argv[2]))
pdict = {
"nregions": [],
"sregions": [fwdpy11.GaussianS(0, 1, 1, 5e-3)],
"recregions": [],
"rates": (0, 1e-2, None),
"demography": fwdpy11.DiscreteDemography(),
"simlen": 40000,
"gvalue": gv,
"prune_selected": False,
}
params = fwdpy11.ModelParams(**pdict)
pop = fwdpy11.DiploidPopulation(5000, 1.0)
rng = fwdpy11.GSLrng(int(sys.argv[1]))
r = GetP()
fwdpy11.evolvets(rng, pop, params, 100, r)
plot_trait_values(r.data)